RPO vs RTO: Key Differences & Why They Matter

In today’s fast-paced digital era, businesses are increasingly dependent on technology to drive their operations and maintain competitiveness. But when systems fail, the consequences can be severe. Unexpected downtime, data loss, or failed backups can cost businesses millions of dollars annually, with some organizations losing as much as $300,000 per hour during an outage. These disruptions harm finances, compromise a company’s reputation, and diminish customer trust.
How can businesses protect themselves from these risks?A strong business continuity plan and disaster recovery strategy are crucial — and at their heart are two important components: Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Understanding RPO vs RTO helps organizations define how much data loss they can tolerate and how long systems can be offline before normal operations are impacted. RPO determines the maximum amount of data loss a business can tolerate in an incident, while RTO measures how quickly operations need to be restored. Together, they address different aspects of recovery while working to ensure business continuity.
In this article, we’ll explore RPO vs RTO, their differences, and why they matter, providing real-world examples, and sharing practical tips to help you define and optimize these objectives for your business.
What is RPO
RPO, refers to the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. In simpler terms, it indicates how far back in time your data can be recovered from backups or replicas after an outage. This helps businesses define their tolerance for data loss, ensuring that data backup and recovery strategies align with operational needs.
For instance, an RPO of one hour means that if a disruption occurs, your organization must restore data from no more than one hour ago, minimizing the impact on critical processes. Setting an appropriate RPO requires businesses to carefully evaluate their applications, databases, and workloads to identify the most critical data needed to maintain normal operations.
Consider an online retail business that processes hundreds of transactions every hour. If this business sets its RPO to two hours, it means it can tolerate losing up to two hours’ worth of transaction data in the event of a failure. However, this tolerance level also assumes that the business has a data backup system capable of restoring operations within this time frame. If data from beyond this two-hour window is lost, the financial and reputational damage could be substantial — emphasizing the importance of setting realistic RPO targets as part of a business continuity plan.
Factors Impacting RPO:
- Data Criticality: Highly sensitive or valuable data, such as customer financial information, requires stricter RPOs.
- Backup Frequency: The more frequently you back up data, the lower your RPO can be. Automated backups play a key role in minimizing RPO.
- Storage Solutions: Leveraging modern storage technologies like cloud-based backups can significantly reduce RPO by ensuring real-time or near-real-time data replication.
What is RTO
RTO defines the maximum time to restore operations after a disruption. Essentially, it’s the deadline recovery—how long your systems can be down before business operations are unacceptably impacted. A well-defined RTO ensures that your disaster recovery plan is effective and aligned with your organization’s capabilities. Without a clear RTO, recovery efforts may falter, leaving critical systems offline longer than manageable, which can severely impact business continuity and customer trust.
To understand the importance of RTO, consider how it directly impacts an organization’s ability to resume operations quickly after a disruption. For instance, during a Black Friday sale, an RTO of two hours might be acceptable on a normal day but disastrous during peak periods, where every minute of system downtime equates to thousands of dollars in lost revenue.
During such high-stakes events, businesses may need to invest in redundant infrastructure or failover systems to meet a tighter RTO. Failing to do so not only results in lost sales but can also damage brand reputation and customer loyalty, especially when customer expectations are at their highest.
Factors Impacting RTO:
- Business Operations Dependency: Critical systems with a direct impact on revenue or customer satisfaction require faster RTOs.
- System Complexity: Complex infrastructures with interdependent components often take longer to restore.
- Recovery Infrastructure: High-availability systems, such as failover clusters and redundant networks, help reduce RTO by enabling faster recovery.
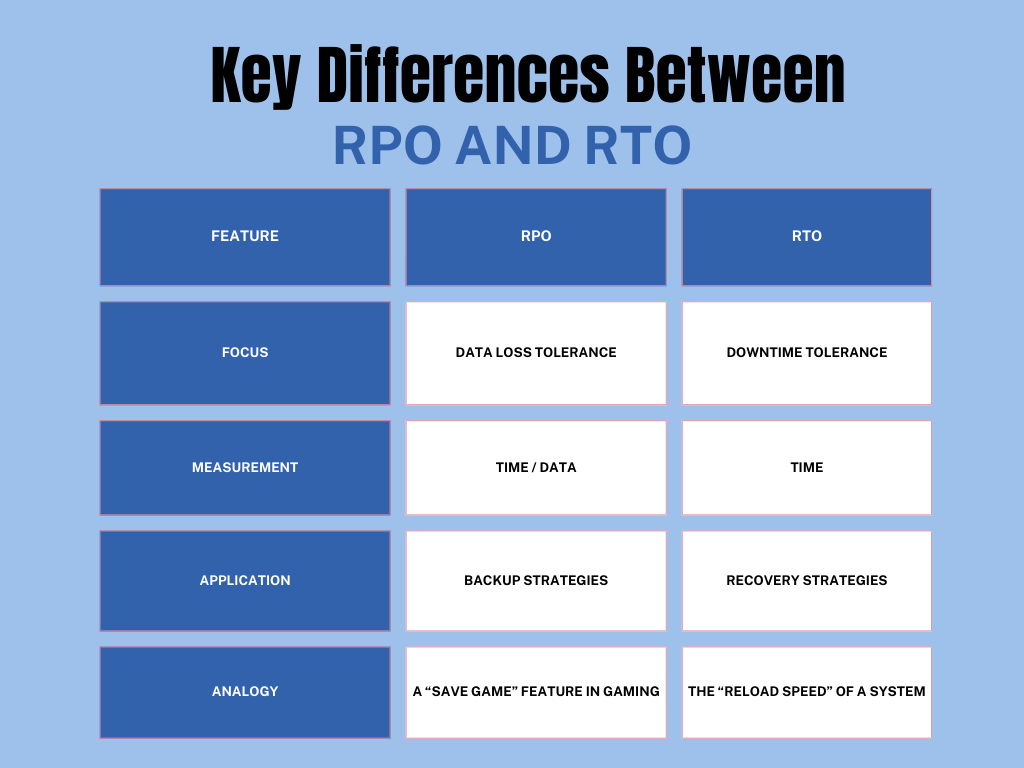
Key Differences Between RPO and RTO
To better understand RPO vs RTO, it’s helpful to compare them side by side:
Both RPO and RTO are crucial in minimizing the impact of outages on your business. While RPO focuses on how much data loss an organization can tolerate, RTO is concerned with how quickly systems must be restored to resume normal operations. Although they address different aspects of recovery, RPO and RTO work together to ensure effective business continuity planning.
Why RPO and RTO Matter for Your Business
Business Impact:
The consequences of insufficient RPO and RTO can be severe
- Customer Trust: Prolonged downtime or data loss can damage a company’s reputation and customer confidence.
- Financial Losses: Downtime costs businesses an average of $5,600 per minute, highlighting the importance of clear recovery objectives.
- Legal and Compliance Implications: Industries such as healthcare and finance face strict data protection regulations. Failing to meet RPO and RTO requirements can result in heavy fines and compliance issues.
Industry Examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals rely on real-time patient data to provide critical care. An RPO of seconds and an RTO of minutes are often necessary to ensure patient safety.
- Finance: Banks and trading platforms handle massive data volumes that demand near-zero data loss and rapid recovery to maintain market integrity.
How to Define and Implement RPO and RTO: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Identify Critical Systems and Data
Determine which systems, applications, and datasets are essential for your operations. Prioritize them based on their impact on revenue and customer experience.
2. Assess Acceptable Downtime and Data Loss
Collaborate with senior management and department leads to establish thresholds for acceptable downtime and data loss.
3. Align RPO vs RTO Goals with Disaster Recovery Strategies
Choose technologies and processes that support your specific objectives. For instance, cloud-based backup and replication can offer lower RPOs and RTOs than traditional on-premises systems.
4. Test and Refine Regularly
Conduct business impact analyses, simulations, and disaster recovery drills to ensure your RPO and RTO targets are achievable, then adjust as needed.
Tools and Solutions:
Modern tools and services can streamline backup processes, reduce RPO, and enable rapid system restoration to minimize RTO. However, managed services providers like Intradyn offer comprehensive data archiving, storage, and disaster recovery solutions, helping businesses maintain resilience and security.
Practical Tips for Optimizing RPO and RTO
Backup Best Practices:
- Automate and Schedule Frequent Backups: Regular data backup helps reduce RPO. Use incremental or continuous backups to save time and storage space.
- Use Offsite and Cloud Storage: Store backups securely offsite or in the cloud to protect against localized disasters or security breaches.
Recovery Planning:
- Invest in High-Availability Systems: Implement redundant servers, load balancing, and failover mechanisms to minimize system downtime.
- Conduct Regular Drills and Simulations: Test your business continuity plan in realistic scenarios to uncover weaknesses and validate response times.
Master RPO and RTO to Minimize Downtime and Data Loss
RPO and RTO are essential metrics for any business continuity or disaster recovery strategy. By understanding their differences and significance, you can build a resilient recovery framework that safeguards your operations, protects customer trust, and ensures compliance with industry standards. Evaluate your current disaster recovery plans, refine your RPO vs RTO objectives, and leverage advanced tools and managed services to reduce downtime and data loss.
Preparation today prevents panic tomorrow. Strengthen your disaster recovery strategy and safeguard your data with Intradyn’s reliable backup, archiving, and business continuity solutions.